Select Your Region
Improved Automotive Refinish Coating Formulations
 |
In the past decade, the United States has observed an average increase of 4.4 million cars operating on its roads each year. Accordingly, the demand for automotive refinish coatings has risen due to more cars requiring damage repairs. |
To account for this increased demand, modern automotive refinish formulations must flawlessly restore the visual beauty of vehicles while facilitating quick turnaround times. In addition, with increasing environmental protective legislation, coating formulators must limit hazardous air pollutants and the environmental impact of their products. Given this, refinish coating formulators need ingredients to help them achieve these demanding end-use requirements.
Solus™ Performance Additive
Eastman manufactures Solus™ 2100 and Solus™ 2300, cellulose acetate butyrate performance additives designed to improve the appearance, efficiency, and environmental compliance of various industrial coatings, including automotive refinish basecoats and topcoats. When used in automotive coating formulations, Solus™ 2100 and 2300 additives impart the following features.
- Faster physical drying and dry-to-touch times
- Better flow, leveling, gloss, and metallic-pigment-flake alignment
- Higher redissolve and strike-in resistance
- Lower solvent demand and compatibility with low-VOC formulations
- Increased bio content incorporation
The following sections outline these features and benefits and present performance data.
Faster Drying
Unlike OEM coatings, which are typically heat cured, refinish coatings are cured in low heat or ambient temperatures, taking longer to complete. Thus, in the case of automotive topcoats and basecoats, it is important to quicken physical drying in formulations to facilitate more refinish jobs and enable polishing steps to be done more quickly after coating.
Since Solus™ 2100 has a relatively high Tg and promotes an exponential rise in viscosity upon cure, it induces rapid dry-to-touch times. This can lead to decreased coating contamination and higher hardness, providing early mar resistance. The data below depicts the effect of adding Solus™ 2100 at 10% to a topcoat system containing an acrylic polyol resin. The reduced coating drying time helps formulators achieve much quicker dry times than industry standards.
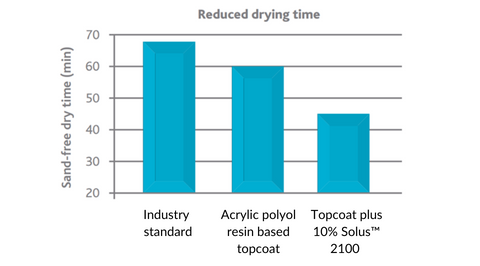 |
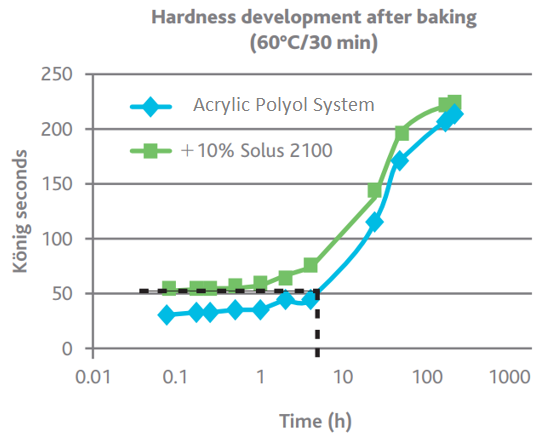 |
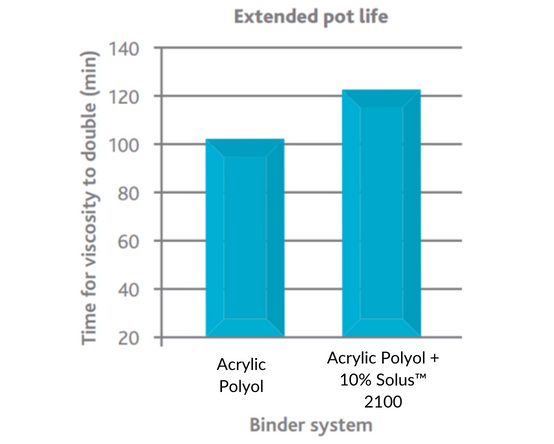 |
The same dry-to-touch time acceleration is also observed in automotive basecoats. Below, the complex viscosity of the coating is shown to increase with higher concentrations of a cellulose acetate butyrate like Solus™ 2100.
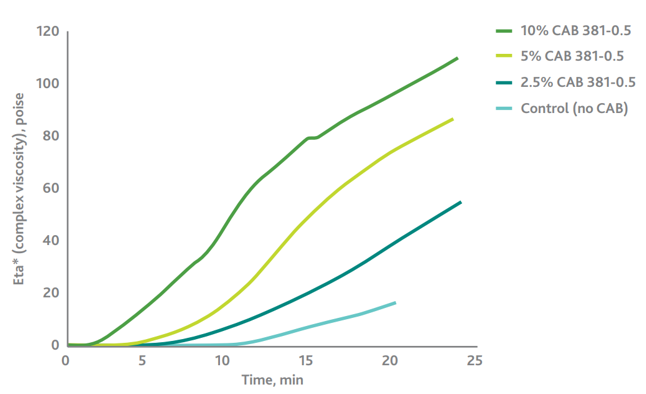 |
Better Visual Quality
Since one of the main functions of automotive refinishes is to restore or improve the aesthetic quality of vehicles, it is crucial that the coatings maximize visual appearance. When it comes to refinish basecoats and topcoats, both the Solus™ 2100 and 2300 additives provide tremendous aesthetic value as flow and leveling agents. These additives also have good wetting properties and influence rheology that reduces surface defects and imperfections. Below is a visual comparison of a clear coat formulation demonstrating the difference in surface appearance Solus™ 2100 provides.
| Flow and leveling of clear coat formulation | |
 |
 |
|
Without Solus™ 2100 |
With Solus™ 2100 |
Solus™ 2100 and Solus™ 2300 also help reduce coating-surface defects due to surface contamination. In the images below, coatings with and without Solus™ 2300 were applied to an automotive substrate contaminated with WD-40. The formulation containing Solus™ 2300 provided a significantly better appearance, indicating that refinish processes can maintain efficiency despite accidental contamination.
 |
 |
| Coating without 5% Solus™ 2300 | Coating with Solus™ 2300 |
The rheology modification that Solus™ 2300 provides yields a critical benefit for refinish basecoat formulations, where metallic pigment alignment is optimized to reflect more light and create a better metallic appearance. Below, microscopy images of basecoats containing metallic pigments with and without Solus™ 2300 are compared for their flop index, an indicator of pigment reflectivity. The formulation without Solus™ 2300 had suboptimal pigment orientation and yielded a lower flop index, creating a visibly darker appearance. In some instances, the optimized pigment orientation Solus™ 2300 provides may lead to lower formulation costs by requiring less pigment to achieve the same metallic effect.
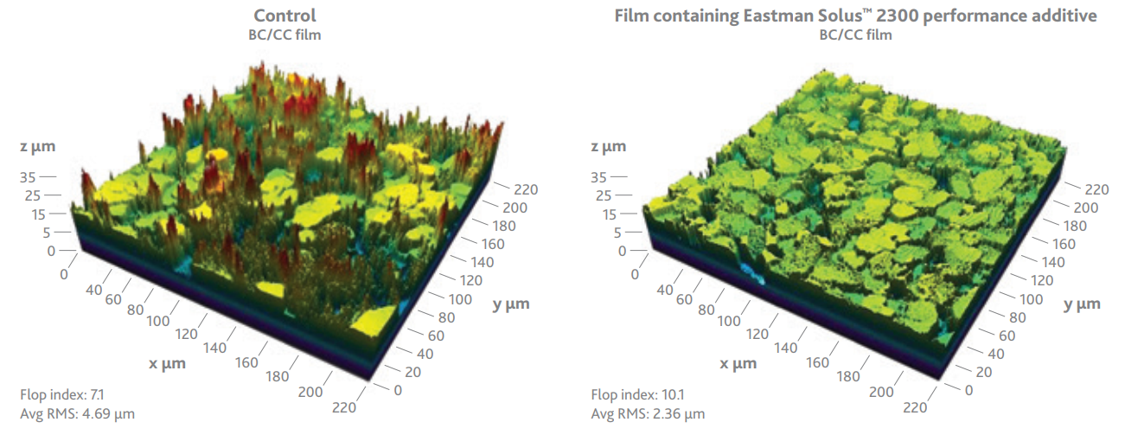 |
The appearance of refinish coatings is also impacted by the interaction of the basecoat and topcoat. Both Solus™ 2100 and Solus™ 2300 provide redissolve and strike-in resistance to the basecoat by preventing solvent migration from the topcoat into the basecoat. SEM images below of the basecoat–topcoat interface help to illustrate the effects of redissolve resistance and pigment alignment that Solus™ 2100 and Solus™ 2300 provide. While not pictured here, the use of Solus™ 2100 or Solus™ 2300 in primers also helps provide redissolve resistance of primers by basecoats.
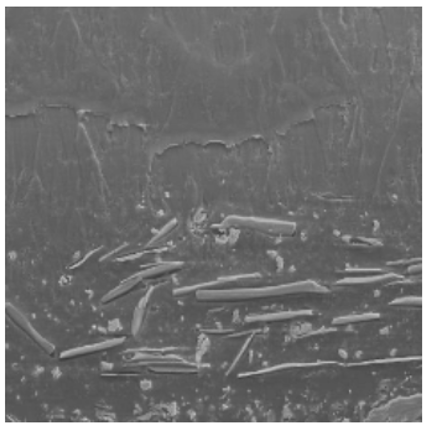 |
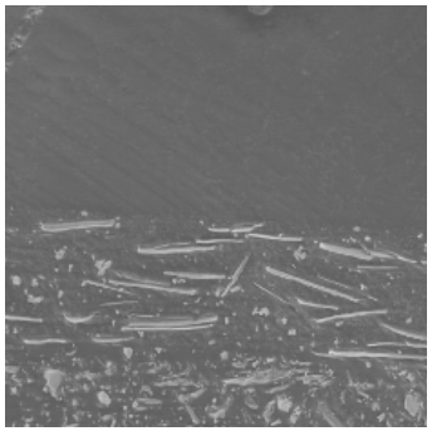 |
|
Without Solus™ |
With Solus™ |
Below, images of a metallic green basecoat with and without Solus™ are shown, where the macroscopic visual impact of redissolve by a topcoat applied can be distinctly seen. Generally, this resistance also provides easier and better color matching.
 |
|||
|
|
Without Solus™ |
With Solus™ |
|
Enhanced Sustainability
Over the past several years, formulations have evolved in response to environmental protection legislation that aims to minimize VOCs produced from refinish coatings. Also, products incorporating sustainability as part of their brand are now better received by automotive customers. Solus™ 2100 and Solus™ 2300 are cellulose acetate butyrate additives specifically designed to help formulators adapt to these modern trends, as these products provide compatibility in formulations that meet lower-VOC requirements while increasing bio content in formulations. The specific features of Solus™ 2100 and Solus™ 2300 that help refinish coating formulators design their products with higher sustainably are listed below.
- Solus™ 2100 and Solus™ 2300 contain an approximate bio content value of 36% and 43%, respectively, increasing the use of renewable raw materials in formulations.
- Solus™ 2100 and Solus™ 2300 are low–molecular weight cellulose acetate butyrate additives with relatively low intrinsic viscosity, reducing solvent demand and VOCs.
- Solus™ 2100 is soluble in Oxsol 100 (PCBTF), a solvent VOC exempted by the US EPA that enables low-VOC formulations.
Summary
Solus™ 2100 and Solus™ 2300 are cellulose acetate butyrate additives designed to increase the efficiency, visual quality, and sustainability of automotive refinish coatings. From efficiency and visual-quality standpoints, they benefit automotive refinishes by inducing rapid dry-to-touch times, reducing surface defects, optimizing metallic pigment flake orientation, and providing resistance to redissolve. In terms of sustainability, these products contain high levels of bio content and feature compatibility with low-VOC formulations through low intrinsic viscosity and solvent demand. Solus™ 2100 takes this a step further by being soluble in the VOC-exempt solvent Oxsol 100. Click below to request a sample or more information and formulation assistance.

Thank you
Thank you for your inquiry and interest in ChemPoint.
We will respond to you shortly.
ChemPoint will not under any circumstances release personal user information to individuals or companies. All information collection is solely used to support ChemPoint customers service communications. Read our Privacy Notice.
Are you in the correct region?
We’ve detected that you are located in a different region than the region selected on the website. Would you like to change your region?
Current Region: English - Canada