Select Your Region
Adhesion Promoters: A Comprehensive Guide
What is an adhesion promoter?
Adhesion promoters are a vast number of chemistries designed to improve adhesion between two materials. Often, they are used in primers or as stir-in additives for coating, paint, ink, and adhesive formulations to minimize the negative impacts of having differences in surface tension of the formulation and the surface energy of the substrate. In the absence of an adhesion promoter, for example, a liquid with high surface tension will tend to bead on surfaces with low surface energy, preventing the necessary wetting and spreading on the substrate to ensure even coverage and form a contiguous film.Why are adhesion promoters necessary?
The substrates that coatings, inks, and adhesives are applied to are increasingly being made of low–surface energy plastics. For example, this is seen in the automotive industry, where plastics have replaced parts traditionally made from metal to lower the overall weight of the vehicle and gain better fuel economy or vehicle range. Other industries, such as building and construction, are also increasingly utilizing plastic materials for fixtures such as roofing, flooring, windows, and insulation to lower costs or increase durability. These parts, fixtures, and materials are typically coated to maximize longevity and improve appearance or fastened using adhesives.How do adhesion promoters work?
As mentioned previously, there are several types of chemistries used as adhesion promoters; thus, the exact mechanism of how each adhesion promoter works differs. In many cases, adhesion promoters form strong bonds between chemical groups present on the adhesion promoter, the substrate, and the liquid formulation being applied. The next sections will cover the distinct properties and mechanisms of several different adhesion promoters.

Organotitanates and Organozirconates
Organotitanates and organozirconates are compounds with titanium or zirconium atoms bonded to organic chemical groups. They form bonds with hydroxyl and carboxyl groups on polymeric substrates and resins present in coating, ink, and adhesive formulations, essentially forming a bridge between the substrates and formulations. Below is a diagram depicting this mechanism. Organotitanates and organozirconates also form bonds well with metal oxides, making them useful in ceramic substrate applications.
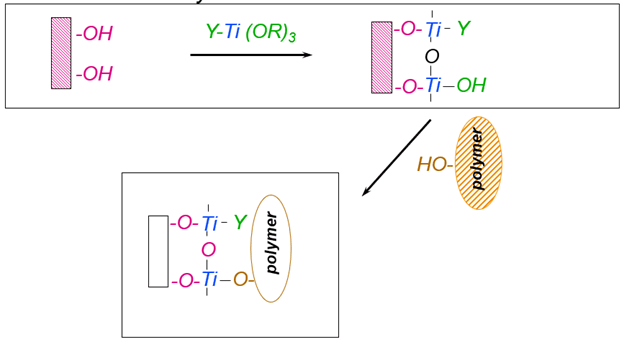
Organosilanes
Organosilanes are bifunctional compounds containing an inorganic reactive group and an organic functional group. The reactive group, which is typically an alkoxy or hydroxyl group, reacts with moisture to form silanol groups, which form siloxane bonds with the substrate. The functional group of the organosilane reacts with chemical groups present on the polymer or polymers that constitute the coating, ink, or adhesive formulation. This mechanism is similar to organotitanates and organozirconates in that they also form a chemical bridge between formulation and substrate.Chlorinated Polyolefins
Chlorinated polyolefins are wax-based compounds functionalized with polar chemical groups on their polymer backbones. These compounds orient themselves in a way where the nonpolar hydrocarbon backbone associates itself with a polyolefin substrate, and the polar groups associate themselves with functional groups present on the coating, ink, and adhesive polymers. Both the backbone and the polar groups form interactions and bonds with the substrates and polymer—again, forming a bridge between the substrate and formulation being applied. Below is a diagram that represents this mechanism.
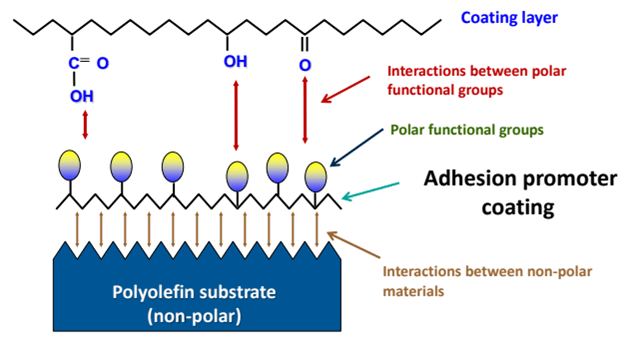
Amines
Polymers and compounds containing amine groups are effective adhesion promoters due to amine-group reactivity with both substrates and chemical groups present on coating, ink, and adhesive polymers. In solutions, amines become protonated and develop cationic charges that enable them to form strong bonds to negatively charged surfaces and functional groups on coating, ink, and adhesive polymers. Below, an image of a hyperbranched amine-rich polymer, polyethylenimine, is depicted forming a bridge between a substrate and functional groups on a polymer.
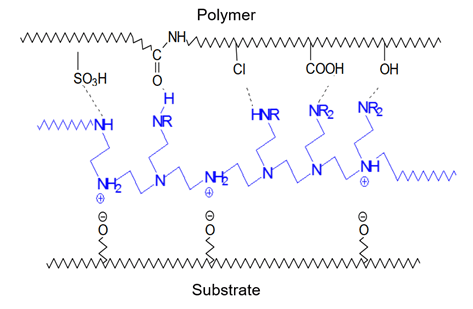
ChemPoint’s Portfolio of Adhesion Promoters
Most of the adhesion promoter chemistries described in this article are available to sample and purchase through ChemPoint.
• Dorf Ketal Tyzor® Organotitanates and Organozirconates
• Eastman Polyolefin Adhesion Promoters
• BASF Lupasol® Polyethylenimine (amine)
ChemPoint is a specialty chemical distributor dedicated to assisting coating, ink, and adhesive formulators with finding the right chemistry for each specific application. Click below to speak to one of our technical sales team members who can help you select the right option.


Thank you
Thank you for your inquiry and interest in ChemPoint.
We will respond to you shortly.
ChemPoint will not under any circumstances release personal user information to individuals or companies. All information collection is solely used to support ChemPoint customers service communications. Read our Privacy Notice.
Are you in the correct region?
We’ve detected that you are located in a different region than the region selected on the website. Would you like to change your region?
Current Region: English - United States