Select Your Region
Vazo™ Initiators for Acrylic Resins
 |
Acrylic resins are among the most widely used in industrial applications ranging from coatings to electronics to eyeglasses, owing to their high degree of durability and optical clarity. The chemical structure of the acrylic polymer has strong covalent bonds in its backbone, relatively small and colorless side groups, and steric hindrance stemming from these side groups. The strong bonds and steric hindrance are responsible for having good resistance to abrasion and deformation, while the side groups create minimal light scattering and absorption, leading to great optical clarity. |
Given the above, it is apparent why acrylic resin manufacturers must carefully control the acrylic polymer structure and prevent resin defects in applications that need to maximize performance. While the purity of acrylic monomers and the curing process of the resin are major factors that influence quality, another factor often overlooked is the quality and type of the free radical initiator.
Initiators for Acrylic Resin Manufacturing
Organic Peroxides
Organic peroxide is the most common free radical polymerization initiator used for resin manufacturing, including acrylic resins. While relatively inexpensive on a pound-for-pound basis compared to other polymerization initiators, it presents a few notable challenges, as listed below.- Vulnerability to radical-induced decomposition, reducing initiator efficiency
- Reactivity with some solvents and redox-sensitive agents, creating more challenging polymerization reaction conditions
- Unpredictability with first-order reaction kinetics, increasing polymerization inefficiency
- Prone to hydrogen abstraction from growing polymer chains, causing defects and reduced yield
- Extreme safety hazards in storage, transport, and handling
There are clear risks associated with using organic peroxides. In addition to the major safety concerns, productivity issues and lower yields are more likely to occur, leading to higher operating expenses.
Azonitrile Initiators
When acrylic resin manufacturers need to maximize the quality and performance of their products, azonitrile-based polymerization initiators, such as Vazo™, are preferred. Vazo™ azonitrile compounds have an N2 central linking group that decomposes into two free radicals under heat or light. In general, Vazo™ initiators offer the following advantages over organic peroxides. These are detailed below.- Potentially more efficient at a lower cost
- Create easier reaction conditions and predictable first-order kinetics
- Higher decomposition temperatures and are not shock sensitive
- Induce a higher yield of polymers with greater control over the structure
Cost
While azonitrile initiators have higher costs than organic peroxides on a pound-for-pound basis in most cases, some peroxides only form a single radical per molecule. In comparison, Vazo™ initiators form two radicals per molecule. Therefore, a strict pound-for-pound price comparison may not be practical since Vazo™ may be more cost-efficient in some cases because it requires less initiator by weight to achieve similar or better efficiency.Ease of Use
As mentioned, organic peroxides are reactive with some solvents and redox-sensitive agents in reaction mixtures. Vazo™ initiators are inert with many other components in reaction mixtures, setting up fewer polymerization reaction condition requirements and making them easier to use. Furthermore, Vazo™ is not dependent on other reaction species or conditions for decomposition. Therefore, Vazo™ always presents predictable first-order decomposition kinetics.Safety
Vazo™ is safer to handle than organic peroxides, which pose explosion hazards if they are not stored under strictly controlled temperatures. In general, Vazo™ compounds have higher decomposition temperatures than organic peroxides and are not shock sensitive, reducing the risk of accidental decomposition and safety hazards. Vazo™ is also a safer chemical to handle, as it has low oral toxicity and will not sensitize skin if touched.Performance
During decomposition, both Vazo™ and organic peroxides form free radicals. However, the hydroxyl radicals formed during the decomposition of organic peroxides are extremely strong oxidizers that easily abstract hydrogen atoms from growing polymer chains. Comparatively, the free radicals that Vazo™ generates do not abstract hydrogen. Using organic peroxides creates radicals at unwanted sites of the polymer, resulting in unexpected branching and polymer quality issues. This reduces yield as the polymer structures become uncontrolled, increasing both polymer molecular weight inconsistency and polydispersity.Vazo™ and Acrylic Resin Manufacturing
Several applications that use acrylic resins will benefit in quality and performance from using Vazo™. Listed below are examples and specific advantages gained by using Vazo™.
Application
|
Benefit
|
|---|---|
Clear coatings and paints
|
|
Windows, lenses, and screens
|
|
Adhesives
|
|
Electronic circuits
|
|
Photoresist coatings
|
|
Vazo™ Grades and Selection
There are several options of Vazo™ initiators based on the reaction medium (e.g., organic solvent or water) and the polymerization reaction temperature. The number associated with each Vazo™ grade name indicates a 10-hour half-life temperature. Generally, grades with a lower initiation temperature tend to have lower color formation in resins.
| Grade | 10-Hour Half-Life Temp (°C)
|
Benefit
|
Molecular Structure
|
Chemical Name
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vazo™ 52 | 52
|
Great in low-temperature polymerizations
|
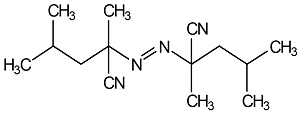 |
2,2’-Azodi (2,4-Dimethylvaleronitrile)
|
| Vazo™ 64 | 64
|
Cost-effective
|
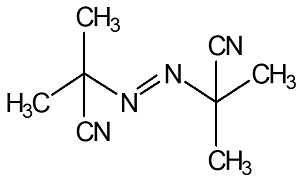 |
2,2’-Azodi (Isobutyronitrile)
|
| Vazo™ 67 | 67
|
Best solubility
|
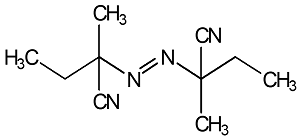 |
2,2’-Azodi (2-Methylbutyronitrile)
|
| Vazo™ 88 | 88
|
Ideal for high-temperature polymerizations
|
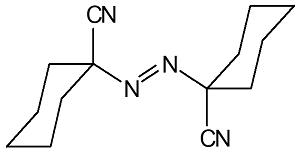 |
1,1-Azodi (Hexanydrobenzonitrile)
|
Vazo™ 56 WSP
|
56
|
Water-soluble
|
 |
2,2’-Azobis (2-Amidinopropane) Dihydrochloride
|
Vazo™ 68 WSP
|
68
|
Soluble in water and organic solvents
|
 |
4,4’-Azobis (4-Cyanovaleric Acid)
|
Summary
Acrylic resins are a top choice in many industrial applications that require excellent durability and optical clarity. Acrylic polymer quality has a direct influence on the performance of products made with acrylic resins, and polymer quality can be heavily impacted by the free radical polymerization initiator. Vazo™ free radical initiators offer several benefits in terms of polymer yield, potential cost savings, ease of use, and safety over initiators such as organic peroxides. As a result, acrylic resins made with Vazo™ become more efficient and safer to produce and tend to be of significantly higher quality. Click below to discuss your resin manufacturing process and learn more about Vazo™ today.

Thank you
Thank you for your inquiry and interest in ChemPoint.
We will respond to you shortly.
ChemPoint will not under any circumstances release personal user information to individuals or companies. All information collection is solely used to support ChemPoint customers service communications. Read our Privacy Notice.
Are you in the correct region?
We’ve detected that you are located in a different region than the region selected on the website. Would you like to change your region?
Current Region: English - United States